graphics-autumn-windmill
graphics-autumn-windmill
Introduction
介绍
This “Autumn Windmill” project is developed by WaterCoFire for the DIICSU DI41008 - Graphics module assignments. Built entirely using C++ and modern OpenGL, this project simulates a fully interactive, three-dimensional environment capturing the serene atmosphere of a rustic autumn landscape. The primary objective was to move beyond simple object rendering to create a cohesive world that integrates procedural geometry, hierarchical animation, and robust asset management pipelines.
这个“秋日风车”是 WaterCoFire 为 DIICSU DI41008 - Graphics(计算机图形学)课程作业开发的项目。该项目完全基于 C++ 和现代 OpenGL 构建,模拟了一个完全可交互的三维环境,旨在捕捉宁静的乡村秋日氛围。项目的核心目标不仅在于简单的物体渲染,更在于构建一个融合了程序化几何生成、层级动画以及稳健资产管理管线的内聚世界。
If you are a DIICSU Comp Sci student
如果您是 DIICSU 计算机专业的学生
This project is for reference only. It lacks creativity, and WaterCoFire strongly encourages you to create originally.
此项目仅供参考。其缺乏创意,WaterCoFire 非常鼓励您原创。
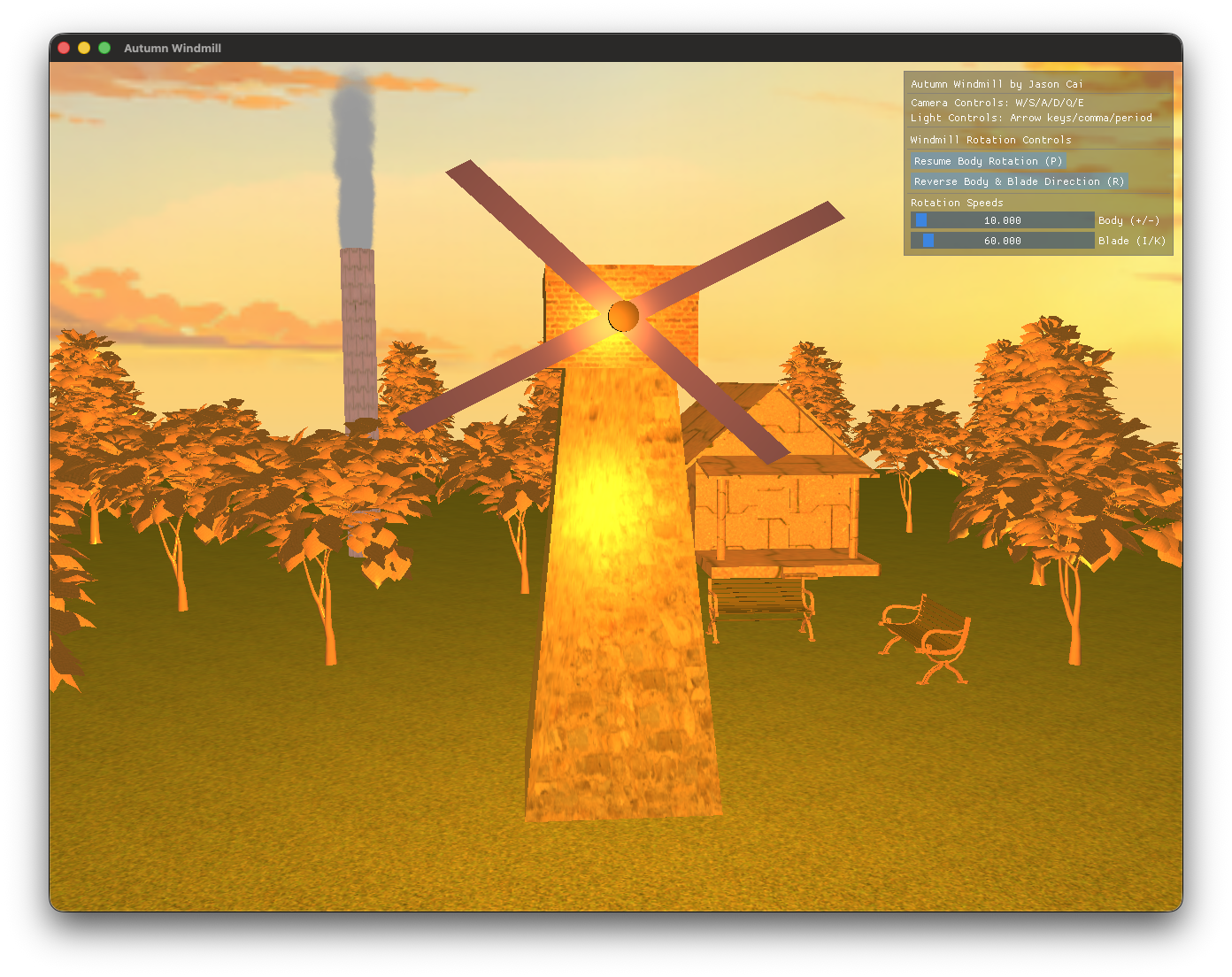
Hybrid Geometry Pipeline
混合几何管线
A distinct feature of this project is its hybrid approach to geometry generation, which balances manual control with algorithmic efficiency. Rather than relying exclusively on imported meshes, the core structures—specifically the windmill tower and cap—are defined through hard-coded vertex arrays to ensure precise architectural control. However, to demonstrate mathematical versatility, complex components such as the windmill’s hub and the smoking chimney were generated programmatically. By utilizing trigonometric functions within the main execution loop, the application dynamically constructs cylinders with variable segment counts, calculating smooth vertex normals for curved surfaces while maintaining flat normals for end-caps to ensure correct shading behavior.
本项目的显著特征在于采用了混合几何生成策略,在手动控制与算法效率之间取得了平衡。项目并未完全依赖导入的网格模型,核心结构——特别是风车塔身和顶盖——是通过硬编码的顶点数组定义的,以确保对建筑形态的精确控制。然而,为了展示数学上的灵活性,风车的轮毂和冒烟的烟囱等复杂组件均由程序化生成。通过在主执行循环中运用三角函数,应用程序动态构建了具有可变分段数的圆柱体,并为曲面计算了平滑顶点法线,同时保持端盖的平面法线,从而确保了正确的光照着色表现。
Scene Composition and Environment
场景构成与环境搭建
As the project evolved from a singular object study into a comprehensive scene, the environment was significantly expanded to include a diverse range of assets. Leveraging the Assimp (Open Asset Import Library), the system ingests external .obj models, successfully populating the landscape with a rustic cabin, wooden benches, and various stylistic trees. To unify these elements into a believable “autumn” world, a skybox was implemented using a cube map texture. A specific depth optimization technique (forcing z=w in the vertex shader) ensures the skybox always renders at the maximum depth, while the ground utilizes GL_REPEAT wrapping modes with high-range texture coordinates to create an expansive, detailed terrain without texture stretching.
随着项目从单一物体研究演变为完整的场景展示,环境得到了显著扩展,包含了多样化的资产。利用 Assimp(开放资产导入库),系统能够摄取外部的 .obj 模型,成功地在景观中添加了乡村小屋、木质长椅以及多种风格的树木。为了将这些元素统一到一个逼真的“秋日”世界中,项目利用立方体贴图实现了一个天空盒。通过一种特定的深度优化技术(在顶点着色器中强制 z=w),确保天空盒始终渲染在最大深度处;同时,地面采用了 GL_REPEAT 包裹模式配合大范围的纹理坐标,从而在不产生纹理拉伸的情况下创造出广阔而细节丰富的地形。
Hierarchical Kinematics
层级运动学
Bringing the scene to life required a robust hierarchical transformation system, specifically designed to handle the complex mechanics of the windmill. The scene graph logic dictates that the windmill’s main body (the tower and cap) rotates around the global Y-axis to simulate orientation changes. Crucially, the blades and the central hub are children of the cap; they inherit this global rotation while simultaneously possessing their own local Z-axis rotation. This implementation resolved early challenges where independent rotations led to spatial misalignment, ensuring that the hub spins perfectly in place regardless of the windmill’s orientation relative to the camera.
为了赋予场景生命力,通过设计一个稳健的层级变换系统,专门用于处理风车的复杂机械运动。场景图逻辑规定风车主体(塔身和顶盖)绕全局 Y 轴旋转以模拟朝向变化。关键在于,扇叶和中心轮毂作为顶盖的子节点,在继承这一全局旋转的同时,还拥有独立的局部 Z 轴自旋。这一实现方案解决了早期开发中因独立旋转导致的空分布局错位问题,确保了无论风车相对于摄像机的朝向如何,轮毂都能在正确的位置完美自旋。
Advanced Rendering and Visual Effects
高级渲染与视觉特效
The visual fidelity of the project is powered by a custom Phong lighting model implemented in the fragment shader, which calculates ambient, diffuse, and specular components per pixel. A critical technical detail was the introduction of a Normal Matrix to correct normal vectors transformed by non-uniform scaling—without this, the lighting on the stretched windmill tower would appear distorted. To further enhance realism, a particle system was engineered to simulate smoke rising from the cabin. Utilizing Instanced Rendering, the system draws thousands of particles in a single call. These particles employ “Billboarding” techniques to ensure they always face the camera, coupled with distance-based sorting and alpha blending to handle transparency without rendering artifacts.
项目的视觉保真度由在片元着色器中实现的自定义冯氏光照模型驱动,该模型逐像素计算环境光、漫反射和镜面反射分量。一个关键的技术细节是引入了法线矩阵来修正受非均匀缩放变换影响的法线向量——若无此修正,被拉伸的风车塔身的光照效果将出现畸变。为了进一步增强真实感,项目设计了一个粒子系统来模拟小屋升起的炊烟。利用实例化渲染技术,系统可以在单次绘制调用中渲染数千个粒子。这些粒子采用了 Billboarding 技术以确保始终面向摄像机,并结合基于距离的排序和 Alpha 混合,在避免渲染伪影的前提下处理透明度。
Interactive User Experience
交互式用户体验
While the initial iteration of the project relied on complex keyboard shortcuts, the final release integrates the Dear ImGui framework to offer a professional graphical user interface. This upgrade transformed the debugging and presentation experience, allowing users to manipulate scene parameters in real-time.
虽然项目的初步迭代依赖复杂的键盘快捷键,但最终版本集成了 Dear ImGui 框架,提供了一个专业的图形用户界面。这一升级彻底改变了调试和展示体验,允许用户实时操控场景参数。
Accessing
访问
This project has been open-sourced on GitHub.
本项目已在 GitHub 上开源。
For reference only. Please consciously refrain from all infringement of others’ IP rights as well as academic misconduct.
仅供参考。请您自觉杜绝一切侵犯他人知识产权以及学术不端的行为。
References
引用
All third-party resources used can be found in the README in the GitHub repository of this project.
所有所使用的第三方资源均可在本项目 GitHub 仓库的 README 文档中被找到。
This post is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0. Credit the source when reposting.
本帖采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议发布。转载请注明来源。
